
Here are a few best practices that can help you optimize Azure storage costs. All REST requests for any type of storage (blobs, tables, queues, etc.) are billed. The third component is the number of requests to the storage account, known as transactions. There is also a fee for data egress – data transfer outside Azure Storage. However, when you access storage services remotely, you’ll pay a fee for access bandwidth usage. If you collocate Azure Storage services with the compute resources that need to access them, you enjoy free bandwidth. The second component is bandwidth, which represents the data transfer rate to the storage account location. Storage is typically computed per GB-month, and the exact fee can depend on the following factors: Azure sums the number of blobs, entities, messages, applications, and metadata it stores to determine total capacity. This is the total amount of data you move to Azure Storage. The first component is storage volume, also known as capacity. Azure Storage pricing consists of three main components.
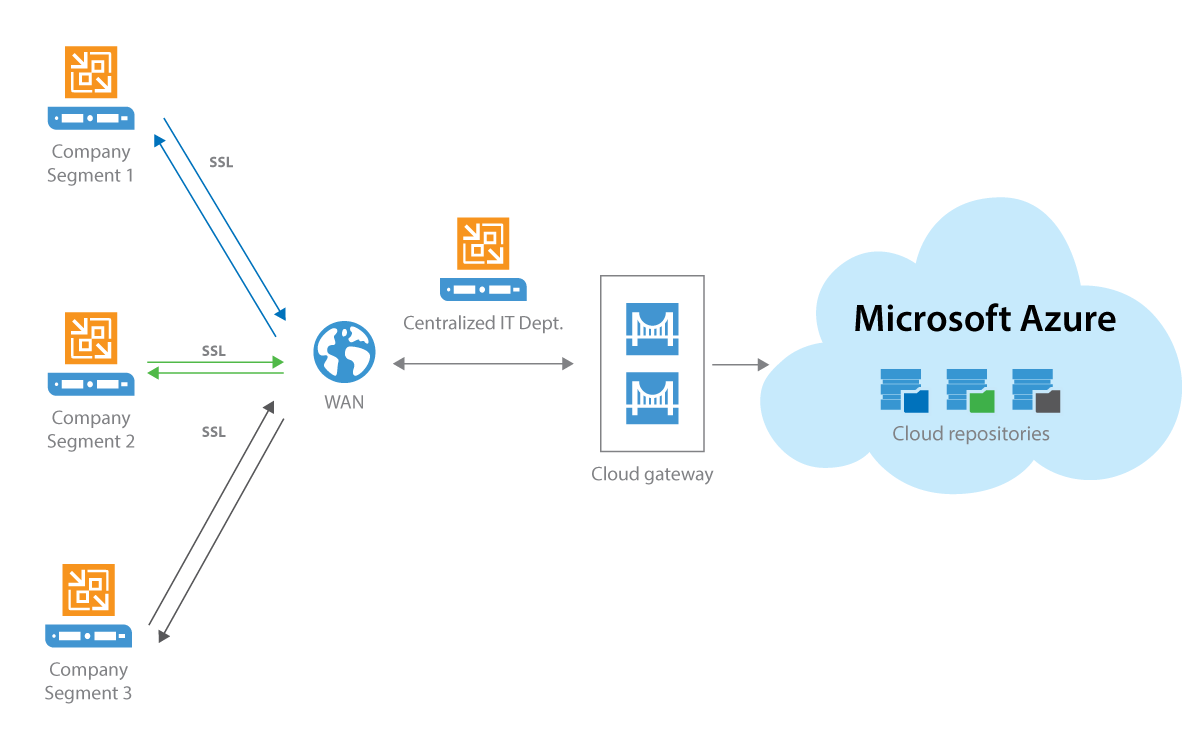
However, customers are still responding to correctly configure access and security, and ensure they back up their data.ĭata in Azure Storage can be accessed from any location via several methods:
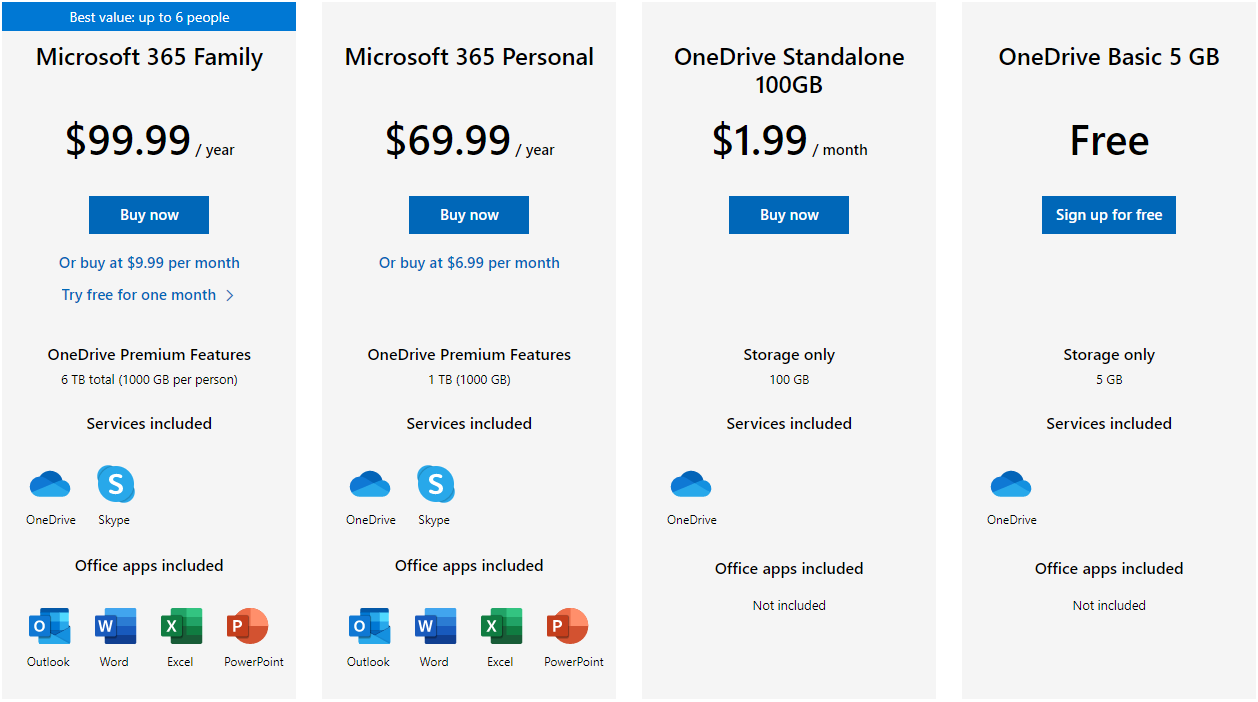
This allows organizations to eliminate the ongoing maintenance and provisioning of storage equipment and servers. Fine-grained controls are available so organizations can control who has access to what data.īecause Azure Storage is a managed service, Microsoft is responsible for the maintenance, regular service updates, and troubleshooting of the Azure Storage service. To support enterprise-grade cloud security, Microsoft designed its infrastructure so that all data written to Azure Storage is automatically encrypted, both at rest and in transit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
